Are you confused by the terms “Megabit” and “Megabyte”? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! It’s like trying to differentiate between a cheetah and a leopard – they may seem similar, but they’re actually quite different. In this blog post, we’re going to unravel the mysteries of Mb vs MB and shed some light on the key differences between these two data units. So, buckle up and get ready to embark on a journey through the world of data measurement – it’s going to be byte-tastic!
Megabit vs Megabyte: A Comprehensive Overview

Megabit vs Megabyte
In the intriguing realm of digital storage and internet speeds, two terms frequently surface, often used interchangeably – Megabit (Mb) and Megabyte (MB). They may appear incredibly similar on the surface, but under the microscope of understanding, they reveal stark differences. Each of these terms represents a unique measure and context within the vast digital landscape. Grab your explorer’s hat as we embark on a journey to decipher the differences between a megabit and a megabyte.
| Megabit | Megabyte | |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | Mb or Mbit | MB or MByte |
| Definition | A megabit equals 10^6 times the unit bit. | A megabyte equals 10^6 times the unit of measure byte. |
| Context of Use | Internet Speeds, Data Transfer Rate | Storage Devices, Size of Files, Storage Capacity |
| Conversion | 1 Megabit = 0.125 Megabytes | 1 Megabyte = 8 Megabits |
Imagine a bustling highway, with vehicles whizzing past at varying speeds. In this metaphor, the megabit symbolizes the speed of the vehicles (data), measuring how swiftly data transfers occur on this digital highway. Conversely, the megabyte represents the size of each vehicle, denoting the file size or storage capacity in our digital devices.
To further clarify, let’s dive into a simple analogy. Picture a librarian (the data transfer process) swiftly moving books (the data) from one shelf to another. The speed at which they move the books equates to megabits, whereas the size of each book they carry signifies megabytes.
For more similar posts like this visit our blog and read about How to Netflix Party on Xbox: A Step-by-Step Guide for Seamless Streaming as well as What Channel is ESPN Plus on Comcast Xfinity? Your Complete Guide.
Understanding this distinction is crucial in the digital era, where every byte and bit count. It helps us make informed decisions when purchasing storage devices, choosing internet service providers, or even simply comprehending the size of the files we share and receive daily.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of megabits and megabytes, exploring their roles in data transfers and storage capacity. Buckle up for an insightful journey into the world of digital measurements!
Megabit: Unraveling the Velocity of Data Transfers

magabit
Imagine you’re on a wide-open highway. The speed at which you’re driving your car represents a Megabit – the unit of measure used to describe the pace of data transfers. In this scenario, the highway is the internet, and your car is the data being transferred. The faster your car (data) moves, the higher the speed in megabits per second (Mbps).
A megabit, often abbreviated as Mb or Mbit, is a cardinal player in the realm of digital information. It’s akin to the fundamental building block, the smallest data unit represented as 0 or 1. A bit is like the microscopic DNA that forms the vast genetic makeup of the digital universe.
When you purchase an internet package from an Internet Service Provider (ISP), you’re essentially buying a highway with a certain speed limit, denoted in Mbps. This speed limit is the rate at which your data car can travel on the internet highway. But remember, a higher speed doesn’t mean your car grows in size; it simply travels faster. The size of the data (car) and the speed of transfer (driving speed) are two different parameters.
Read all about: How to Host the Ultimate Netflix Party with Video Call: A Complete Guide
Picture this: a librarian (your ISP) promises to deliver books (data) to your doorstep. The speed at which the librarian runs (Mbps) doesn’t inflate the size of the books. It merely affects how quickly you’ll receive them. So when your ISP sells you an internet package with a greater Mbps, it’s essentially promising a swifter delivery of the same size of data.
Grasping this concept is crucial in the digital age, where internet speeds are a vital part of our daily lives – be it for streaming your favorite show, downloading a hefty file, or simply browsing the web. The understanding of Megabits enables you to make an informed decision when choosing an ISP or understanding your internet connection’s efficiency.
However, a Megabit and a Megabyte, despite sounding similar, serve different functions in the digital realm. While we have acquainted ourselves with the role of a Megabit in data transfers, let’s delve deeper into the role of a Megabyte in file size and storage capacity in the next section.
Megabyte: The Size of Files and Storage Capacity
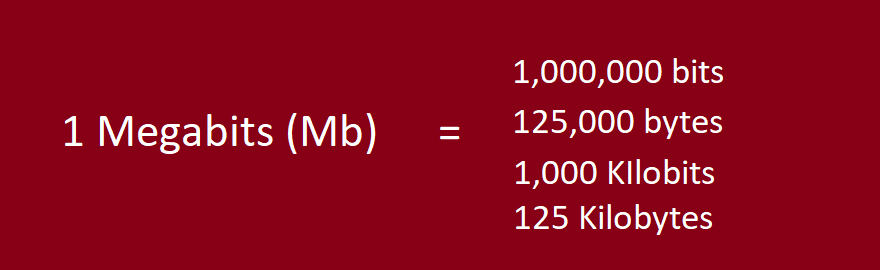
megabit
Imagine you’re a librarian. Your library is filled with books of all shapes and sizes. Each book represents a file on your computer, and the library itself symbolizes your computer’s storage capacity. The size of each book is measured in megabytes (MB or MByte).
Read more about: “Looking for the Best Wired Routers in 2023? Discover the Top 7 Non-Wireless Options Without WiFi!” as well as “Want to Cancel Spectrum Services? Here’s Your Ultimate Guide to Ending Internet, TV, and Mobile Subscriptions”.
Megabytes are the language we use to express the size of these digital books. Whether it’s a photo from your last vacation, a spreadsheet for work, or a favorite song, each file has a size, and that size is measured in megabytes.
Just as you might measure the area of a room in square feet or the distance between two cities in miles, we use megabytes to measure the size of digital files. And just as a byte is composed of 8 bits, a megabyte is comprised of 10^6 bytes. This is the yardstick by which we measure the digital realm.
Read all about: “Why is Your Xfinity Modem/Router Blinking White? Find Out the Meaning, Reasons, and Fixes”
But megabytes don’t just tell us about file size. They also give us insight into the storage capacity of our devices. When you look at the specifications of your laptop, for instance, you’ll see the storage capacity of its Random Access Memory (RAM) and Hard Disk Drive (HDD) expressed in megabytes or gigabytes (thousands of megabytes).
Furthermore, they play a crucial role in indicating how swiftly data can be read from or written to storage devices. This speed is measured in megabytes per second (MB/s).
So, think of megabytes as the measuring tape we use to comprehend the digital universe. They help us understand the size of our files, the capacity of our storage devices, and the speed with which we can access or save our data.
Decoding the Digital DNA: The Ratio Between Bits and Bytes
Megabit vs Megabyte
Imagine you’re in a digital universe, where data is the DNA. This DNA is composed of bits and bytes, and the relationship between them forms a critical part of this digital genetic code. Just as our DNA has a unique sequence of genes, the digital world has a unique ratio between bits and bytes.
At the heart of this digital universe is a fundamental principle: 1 byte equals 8 bits. This principle is as constant as the speed of light in physics, and it scales uniformly across all units of digital data. Therefore, 1 kilobyte (KB) equals 8 kilobits (Kb), 1 megabyte (MB) corresponds to 8 megabits (Mb), and the pattern continues unbroken up to terabytes and beyond.
Now, let’s apply this principle to a real-world scenario. Suppose you’re on the digital highway with an internet speed of 1 Mbps, or 1 megabit per second. With this speed, your internet connection can transfer a mere 0.125 megabytes of data each second. That’s approximately the size of a small, low-resolution image. However, if you ramp up your speed to 8 Mbps, you can transfer 1 megabyte of data per second, allowing you to send or receive larger files, like high-resolution photos or short video clips, in the blink of an eye.
Understanding the ratio between bits and bytes is like learning the rules of the road in the digital universe. It helps you make informed decisions about your internet package and enables you to comprehend the efficiency of your internet connection.
So, the next time you’re considering an internet package or trying to understand why a file takes a certain time to download or upload, remember this ratio. It’s the key to unlocking the mysteries of the digital world and making the most of your online experience.
Converting Megabytes to Megabits: The Digital Conversion You Need to Know
Just as you would convert miles to kilometers or pounds to kilograms while traveling abroad, the digital world also requires its own form of conversion. This is where the process of converting megabytes to megabits comes into play. This process is not as complex as it may sound. In fact, it’s as simple as multiplying by 8: a ratio that might remind you of a chorus from a popular children’s math song.
“One, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight. Multiply by 8, and you’ll never be late!”
That’s right! For every megabyte, there are 8 megabits. This is a fact that’s as constant as the sun rising from the east. So, if you have 1 megabyte, you can quickly calculate that you have 8 megabits. If you have 4 megabytes, that’s equivalent to 32 megabits. Scalable for any number, you can see that 100 megabytes would then be equal to a whopping 800 megabits.
Why is this conversion so important? Think of it as the bridge connecting two crucial aspects of our digital lives: internet speeds and file sizes. Internet speeds are usually measured in Mbps (megabits per second), while file sizes are typically measured in MB (megabytes). This conversion helps us compare these two quantities in the same unit, and thus make sense of our digital universe.
Remember: The key to understanding the digital world is in the details. 1 Megabyte (MB) equals 8 Megabits (Mb). This ratio is the cornerstone of comprehending data sizes and internet speeds.
So, the next time you’re looking at your internet package or trying to understand how fast your large files will download or upload, remember the magic number 8. This simple multiplication can provide you with the knowledge and understanding to navigate the digital world more efficiently.
Data Measurement: From Bits to Terabytes

terabytes
Imagine you’re standing at the foot of a mountain, peering up at the rocky terrain. The mountain represents the vast digital landscape, and the pebbles under your feet symbolize the smallest units of data, the bits. Now, imagine gathering 1,000 of these pebbles together. You’ve just created what we in the digital world call a kilobit.
Read more about: Is 25 Mbps Fast Enough for Gaming, Streaming, and More? A Comprehensive Guide
Let’s continue our journey up the mountain, where we find larger rocks, each representing a bigger unit of data. Gathering 1,000 kilobits together, we create a megabit. Climbing higher, we reach boulders, the gigabits, each equivalent to 1,000 megabits. And finally, at the top of the mountain, we see a massive monolith, representing a terabyte – a whopping 1,000 gigabits.
Also check out: “Is Your AT&T Fiber WiFi Signal Weak? Discover the 7 Best WiFi Extenders for 2023 and Boost Your Connection with These Top Picks”
But that’s just half the story. As we trace our way back down the mountain, we find another path, one scattered with bytes instead of bits. The conversion here follows the same principle: 1,000 bytes make up a kilobyte, 1,000 kilobytes equal a megabyte, 1,000 megabytes form a gigabyte, and 1,000 gigabytes give us a terabyte.
It’s important to remember that while climbing up this mountain of data, we’re not just scaling up in size, but also in the potential for storage and information transfer. With each step, we’re expanding our digital capabilities, moving from bits to bytes, kilobytes to megabytes, and gigabytes to terabytes.
By understanding these units of digital measurement, you’re better equipped to make informed decisions about your internet package, gauge the speed of your connection, and manage your digital storage needs. The digital world may seem like a mountain, but with a solid grasp of these fundamental measurements, you’ll find it’s a mountain you can climb.
Megabytes vs. Megabits: The Intricacies of Speed and Size
Megabit vs Megabyte
Imagine you’re standing in front of a massive digital library, brimming with books, movies, music, and games. Each of these digital entities comes with a data size, measured in megabytes (MB). Now, envision a high-speed conveyor belt, transporting these digital items to your device. The swiftness of this belt is measured in megabits per second (Mbps).
The critical distinction to understand here is that a megabyte is faster than a megabit. When it comes to digital data, size and speed are two different aspects. To put it simply, 1 megabyte equals 8 megabits. Hence, a file size of 100 MB is not the same as an internet speed of 100 Mbps. The former quantifies the size of your digital content, while the latter refers to the speed at which this content reaches your device.
Remember, a larger file size doesn’t necessarily mean a longer download time. The download duration depends on the speed of your internet connection, not the weight of the file.
Let’s consider a practical example. Suppose you’re downloading a movie with a file size of 800 MB. An internet speed of 100 Mbps doesn’t mean that your movie will be ready in 8 seconds. This is because the speed mentioned here is in megabits, not megabytes. Therefore, you need to divide the file size by the speed (after converting it to megabytes) to get the estimated download time.
The conversion from megabits to megabytes, and understanding the difference between the two, plays a crucial role in your digital experience. From choosing the right internet package to deciding on your digital storage needs, these units of measurement are the hidden power players in the digital realm.
Read all about: Is 50 Mbps Fast Enough in 2023? A Detailed Practical Analysis of Internet Speeds
So, the next time you’re downloading your favorite series or uploading your work files, remember to look beyond the file size. Consider the speed at which your internet can transport these digital entities. The world of megabytes and megabits is more than just numbers; it’s about the speed and size of your digital universe.
Comparing Megabytes, Gigabytes, and Terabytes
Imagine standing at the base of three towering mountains, each one significantly taller than the last. The first, a lofty hill, represents a megabyte (MB). The second, a formidable peak, embodies a gigabyte (GB), and the third, an awe-inspiring summit, signifies a terabyte (TB). This visual analogy beautifully illustrates the hierarchy of data measurements, where each unit of measurement dwarfs the preceding one.
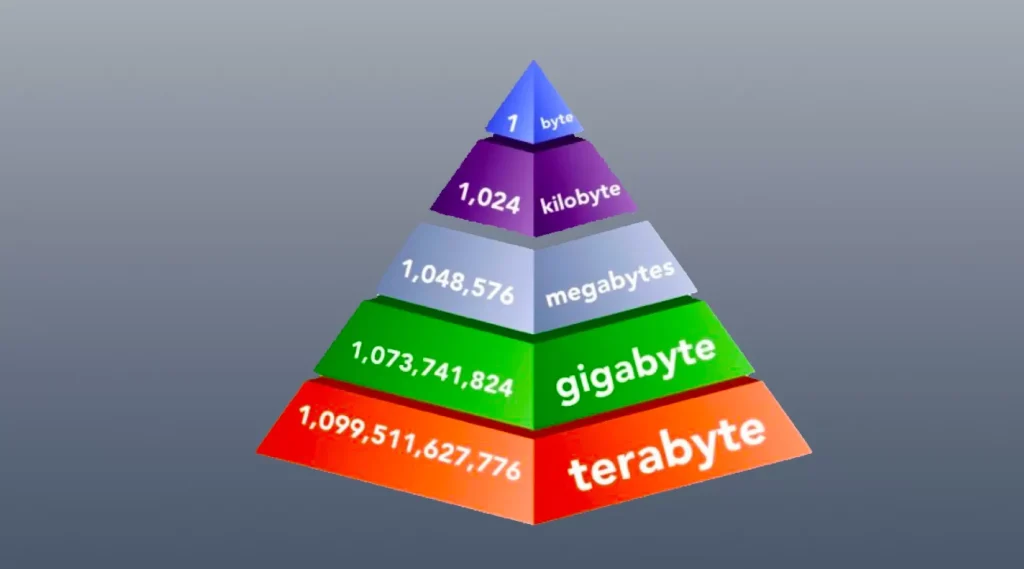
In the digital landscape, this hierarchy is clearly defined: 1 gigabyte equals 1,000 megabytes, and 1 terabyte equals 1,000 gigabytes. It’s akin to saying that a thousand hills make up a mountain, and a thousand mountains create a massive range. Yet, these measurements are not just about size. They also denote the volume of data that can be stored or transferred, affecting how we interact with digital content.
Note: When gauging the size of your digital mountains, remember that 1 GB is equivalent to 1,000 MB, and 1 TB equals 1,000 GB.
But, why does this matter, you may ask? Consider this: knowing the difference between these units is like understanding the difference between climbing a hill, a mountain, or a mountain range. It can help you estimate how much digital equipment you’ll need, the time it will take to transfer files, and the cost of storing your data. In essence, it is a vital piece of knowledge for anyone navigating the digital terrain.
Read about: “Which Hotspots Will Give You the Best Gaming Experience in 2023? Discover the Top 8 Low Ping/Latency Destinations!” as well as How Can I Easily Return Xfinity Equipment for All Services?
So, whether you’re managing personal files, running a business, or planning a comprehensive data strategy, understanding these units of measurement can be your compass, guiding you through the vast landscape of digital storage and transfer.
With this knowledge, you can confidently scale the peaks of megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes, conquering any digital challenge that comes your way.
Conclusion
Imagine being a digital architect, constructing your own unique space in this interconnected world. Each day, you navigate through a labyrinth of information, build bridges of communication, and create edifices of knowledge. As an architect of your digital domain, understanding the building blocks is vital. Megabits and megabytes are two such building blocks that form the basis of your digital existence.
These two units of measurement may seem small, but their significance is massive. Whether you’re racing against time to submit a project or leisurely streaming your favorite movie, the speed of your internet connection and the size of the files you handle are pivotal. These speeds and sizes are measured in megabits and megabytes respectively. Knowing the difference between these two units can help you optimize your digital experiences.
When choosing an internet package or deciding on a storage device, it’s like choosing the wheels for your vehicle or the bricks for your home. The wrong choice can lead to confusion, frustration, and unnecessary expenses. However, with the knowledge of megabits and megabytes, you can avert these pitfalls. You can make well-informed decisions about your digital needs, ensuring your journey through the digital landscape is smooth and efficient.
In conclusion, the disparity between a megabit and a megabyte may seem minuscule, but understanding this difference carries significant implications in the digital realm. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you become a true master of your digital domain, capable of making informed decisions and maximizing your digital potential.
Q: What is the difference between Megabit (Mb) and Megabyte (MB)?
A: Megabit refers to the speed of data transfers, specifically internet speeds, while Megabyte is used to measure the size of files and the storage capacity of RAM and HDD.
Q: How are Megabit and Megabyte abbreviated?
A: Megabit is abbreviated as Mb or Mbit, while Megabyte is abbreviated as MB or MByte.
Q: What is the difference between a bit and a byte?
A: A bit is the smallest data unit in computers and digital information, represented as 0 or 1. A byte, on the other hand, is the basic unit of measurement in computer storage and processing, consisting of 8 bits.
Q: How do you convert Megabytes to Megabits?
A: To convert Megabytes to Megabits, you multiply the units by 8. For example, 1 Megabyte is equal to 8 Megabits.
