Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of digital storage? Well, buckle up because today we’re going to settle the age-old debate: Gigabytes (GB) versus Megabytes (MB). Picture this: you’re staring at your computer screen, trying to decide which file size is bigger. Is it a Gigabyte or a Megabyte? It’s like trying to choose between a jumbo-sized pizza or a regular one. But fear not, my tech-savvy friends, because in this blog post, we’re going to break it all down for you. Get ready for a byte-sized adventure that will leave you saying, “Oh, now I get it!” So, let’s jump right in and unravel the mysteries of Gigabytes and Megabytes.
Understanding the Basics: Gigabytes and Megabytes
Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
When delving into the world of digital storage, two terms frequently surface – Gigabyte (GB) and Megabyte (MB). But what do these terms truly signify, and how do they stack against each other? In essence, a Gigabyte is 1000 times larger than a Megabyte. This vast discrepancy not only sets them apart but also greatly impacts their application and usage.
Imagine you’re standing at the foot of a towering skyscraper, craning your neck to see the top – that’s akin to a Megabyte peering up at a Gigabyte. The difference in their magnitude is as stark as the contrast between a single grain of sand and an expansive desert. A Gigabyte’s colossal size relegates it to heavy-duty tasks. It is the designated carrier for large files such as 4K movies, intricate 3D renders, and immersive video games. In contrast, the smaller, more nimble Megabyte is perfect for medium-sized files.
Read all about: How to Get a Netflix Free Trial Without a Credit Card or PayPal: A Step-by-Step Guide
To truly comprehend the disparity in their sizes, we need to delve a bit into their structure. A Megabyte encompasses 1 million bytes, while a Gigabyte engulfs a whopping 1 billion bytes. To put it into perspective, if bytes were drops of water, a Megabyte would barely fill a bathtub, while a Gigabyte could easily flood a small house.
Let’s break it down further:
| Unit | Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 1 Byte | 8 binary digits (bits) |
| 1 Megabyte (MB) | 1 million bytes |
| 1 Gigabyte (GB) | 1 billion bytes |
| 1 Terabyte (TB) | 1024 Gigabytes |
| 1 Petabyte (PB) | 1024 Terabytes |
| 1 Exabyte (EB) | 1024 Petabytes |
| 1 Zettabyte (ZB) | 1024 Exabytes |
| 1 Yottabyte (YB) | 1024 Zettabytes |
Understanding the vast difference in size between a Megabyte and a Gigabyte is fundamental in grasping how data is stored and manipulated in the digital world. It provides a lens through which we can appreciate the immense capacity of our devices and the complex tasks they can accomplish.
Unraveling the Roles of Gigabytes and Megabytes in Our Digital Universe

Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
Have you ever marveled at how vast our digital universe is? From the stunning 4K movies that transport us to other realms, to the captivating 3D renders that bring our imagination to life, it’s a universe teeming with wonders. Behind these marvels, often hidden in plain sight, are two indispensable units of digital measurement – the Gigabyte and the Megabyte.
Read all about: How do i log into my router without a password or username?
Let’s begin our journey by taking a closer look at the Gigabyte (GB). The Gigabyte, akin to a vast ocean in our digital world, is typically used to denote large-sized files. The 4K movies that offer us an immersive cinematic experience? They are measured in Gigabytes. Those visually stunning 3D renders and large-scale games that whisk us to fantastical realms? You guessed it, they also fall into the Gigabyte category.
But the Gigabyte isn’t just about massive files. It also plays a pivotal role in representing the storage capacity of our digital devices. When we talk about the RAM in our computers, or the hard drives that safely store our memories and work, we’re venturing into the territory of Gigabytes. It’s hard to imagine our digital lives without this colossal unit of measurement.
Read all about: Is 100 Mbps Fast Enough for 2023? Discover the Capabilities and Performance as well as “Is 1000 Mbps Still Fast in 2023? Discover the Truth with an Infographic and Practical Insights”.
Next, let’s turn our attention to the Megabyte (MB). If the Gigabyte is the ocean, then the Megabyte is the river that feeds into it. It’s smaller, but no less important. Megabytes are typically associated with medium-sized files – those items that require a significant amount of storage, but aren’t quite as large as their Gigabyte counterparts.
Think about the high-definition photos that capture our precious moments, the short videos that make us laugh, the mobile applications that make our lives easier, or the songs that resonate with our emotions. All these are typically measured in Megabytes. While they may not be as colossal as Gigabytes, they are integral to our digital universe.
Understanding the roles of Gigabytes and Megabytes in our digital universe is not just about numbers, it’s about comprehending the scale and capacity of our digital experiences. It’s about realizing the immense storage required to bring our digital wonders to life. So, the next time you watch a 4K movie or click a high-definition photo, remember, you’re not just consuming content, you’re exploring the vast expanse of our digital universe.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Gigabytes and Megabytes

Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
As we delve deeper into the world of digital data storage, let’s take a moment to dissect the complex structures of Gigabytes (GB) and Megabytes (MB). Picture these units as building blocks, each one composed of smaller elements, much like a tower of digital legos.
Megabytes (MB), often associated with medium-sized files such as high-resolution images or short videos, are substantial in their own right. But what makes up a Megabyte? Well, imagine a small city, teeming with life. In this city, each house represents a Kilobyte (KB). Now, there are precisely 1024 of these ‘houses’ or Kilobytes in our ‘city’ or Megabyte. To make it even more relatable, consider each Kilobyte as a page of a book. So, a Megabyte is a thick volume containing a whopping 1024 pages!
Think of a Megabyte as a bustling city filled with 1024 houses, or as a hefty book with 1024 pages.
Now, let’s step up to the larger and more imposing Gigabytes (GB). These are the heavyweights of the digital realm, commonly associated with larger files such as 4K movies, comprehensive 3D renders, or even the storage capacity of your laptop or smartphone. A Gigabyte is equivalent to 1024 Megabytes. So, if Megabytes are cities, Gigabytes would be countries, each made up of 1024 cities! Or, in our book analogy, a Gigabyte would be a grand library housing 1024 hefty books!
Envision a Gigabyte as a vast country composed of 1024 cities, or a grand library filled with 1024 thick volumes.
To sum up, these units of digital data, though invisible to the naked eye, form the very backbone of our virtual experiences. Understanding their composition helps us comprehend the sheer scale of digital data storage, making us more informed users in this ever-expanding digital universe.
Decoding the Language of Data Storage

Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
Just as we use languages to communicate and understand each other, our digital devices too have a language, a language of data storage. This language helps our devices to store and retrieve information efficiently. The most basic unit of this language is a byte. But wait, what is a byte? Let me break this down for you.
For more smilar posts like these visit our blog and check out How many mbps do i need for zoom? as well as Does netflix come free with xfinity?
Imagine a byte as a digital packet. This small packet has the capacity to hold eight tiny slots of information, each termed a ‘bit’. The bits act like the 1s and 0s, which are the building blocks of all digital data. And guess what? This tiny packet, the byte, is the cornerstone of all data storage.
Simply put, a byte is a collection of 8 bits.
Now, let’s consider a scenario where you need to store a larger amount of information. Would you rather have millions of individual bytes floating around, each carrying a minute piece of information, or would you prefer a more organized system? This is where Kilobytes (KB), Megabytes (MB), and Gigabytes (GB) come in.
Imagine a Kilobyte as a digital city. It’s a unit of the byte family that contains 1024 individual houses, each house being a byte. Moving up the hierarchy, a Megabyte can be viewed as a digital country, housing 1024 cities or Kilobytes within its borders. The progression continues with a Gigabyte, which can be likened to a continent containing 1024 countries or Megabytes.
| Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Byte | 8 bits |
| Kilobyte (KB) | 1024 bytes |
| Megabyte (MB) | 1024 Kilobytes (KB) |
| Gigabyte (GB) | 1024 Megabytes (MB) |
In essence, each unit of data storage is 1024 times larger than the preceding one, forming a digital hierarchy of information. This means that a Megabyte equates to a whopping 1 million bytes, while a Gigabyte blows this figure out of the water with a staggering 1 billion bytes.
In the world of digital data storage, understanding these units – bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes, and Gigabytes – is key to comprehending the scale at which our digital lives operate. From the smallest text file to the largest video game, every piece of digital data we interact with is measured in these units.
Frequently Asked Questions: Navigating the World of Gigabytes and Megabytes
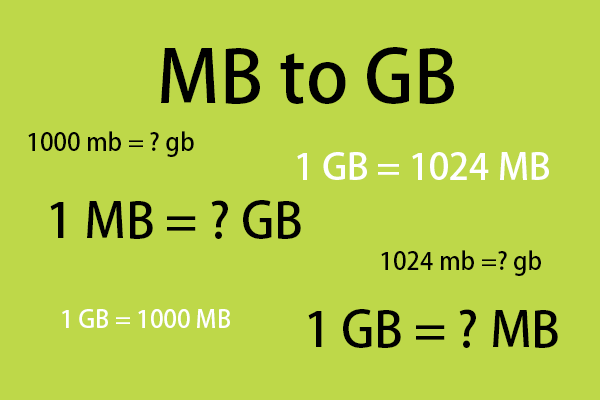
Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
As we delve deeper into the realm of digital data storage, it’s only natural to have a series of questions pop up. It’s a vast landscape, much like exploring an unknown city or stepping foot on a foreign continent for the first time. Let’s address some of the most common queries that surface in this intriguing world.
How many GB makes 1 MB?
In the world of data storage, just as 1000 meters make up one kilometer, 1024 MB (Megabytes) compose 1 GB (Gigabyte). It’s like comparing the size of a city (MB) to the size of a country (GB). The Gigabyte is a much larger unit, encompassing a multitude of smaller units, the Megabytes.
How many hours does it take to use 1 GB of data?
This question is akin to asking how long it takes to traverse a country. It largely depends on your mode of transportation, or in this case, factors such as internet speed, router capacity, and the specification of the client device. Imagine you’re journeying at a speed of 10Mbps (Megabits per second). In this scenario, it will take you approximately 14 minutes to download 1 GB of data. Remember, just as with any journey, your speed can significantly affect your travel time.
Which is the largest unit of storage in a computer?
If we were to compare data storage units to geographical scales, Yottabyte would be akin to our entire globe. It’s the largest unit of storage in the metric system. However, as technology currently stands, the largest storage drives we’re using are in the terabytes range. It’s like we’ve explored up to the size of continents (Terabytes), but not yet the entire globe (Yottabytes).
Read all about: How to Troubleshoot and Resolve Orbi Blinking White Light Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
As we continue to unravel the intricacies of digital storage units, remember that these measurements are not just abstract concepts. They’re the building blocks that allow us to store, share, and experience digital content in our everyday lives. From storing family photos to downloading your favorite 4K movies, understanding these units is key.
Conclusion

Gigabyte (GB) vs Megabyte (MB)
In the vast landscape of digital storage, where bytes make up the terrain and data forms the mountains and valleys, two units of measure stand tall: Megabytes (MB) and Gigabytes (GB). These are the yardsticks by which we quantify, manage, and exchange our digital world. Given the sheer scale of our data-driven lives, understanding these units is akin to learning the language of a new country. It’s not just about knowing the words; it’s about understanding their place in the grand scheme of things.
The Gigabyte, the Goliath of the two, is a thousand times larger than its companion, the Megabyte. This difference in size typically earmarks GB for the heavy-lifting – storing voluminous 4K movies, intricate 3D renders, expansive games, and more. On the other hand, MB, being smaller, often takes care of medium-sized files and tasks.
One might wonder, if GB is larger, why not use it all the time? Well, it’s like using a bulldozer to plant a flower – sure, you could, but it’s not quite the right tool for the job. Using the appropriate storage unit allows us to understand and manage our digital resources better. It helps us make the most of our technological allies, be it a humble flash drive or a high-powered gaming rig.
Also check out: “1500+ Funny WiFi Names in 2023: Unleash Your Creativity and Stand Out!”
As we look to the future, it’s exciting to think about the potential evolution of data storage. With technology advancing at an unprecedented pace, it’s not hard to imagine a day where GB and MB might be overshadowed by larger units. However, for now, they reign supreme, guiding us through the digital frontier.
So whether you’re a casual user browsing the web or a tech enthusiast building your next rig, understanding the difference between MB and GB can empower you. It can help you make informed decisions, optimize your storage, and navigate the digital world with ease and confidence.
Q: What is the difference between Gigabyte (GB) and Megabyte (MB)?
A: Gigabyte (GB) is 1000 times larger than Megabyte (MB).
Q: What are some examples of files that are measured in Gigabytes?
A: Gigabyte is used to denote large sized files such as 4K movies, 3D renders, games, etc.
Q: What are some examples of files that are measured in Megabytes?
A: Megabyte is used for medium sized items such as HD photos, short videos, mobile applications, songs, etc.
Q: How many kilobytes are in a Megabyte?
A: Megabyte is equal to 1024 kilobytes, which are themselves made of 1024 bytes.
